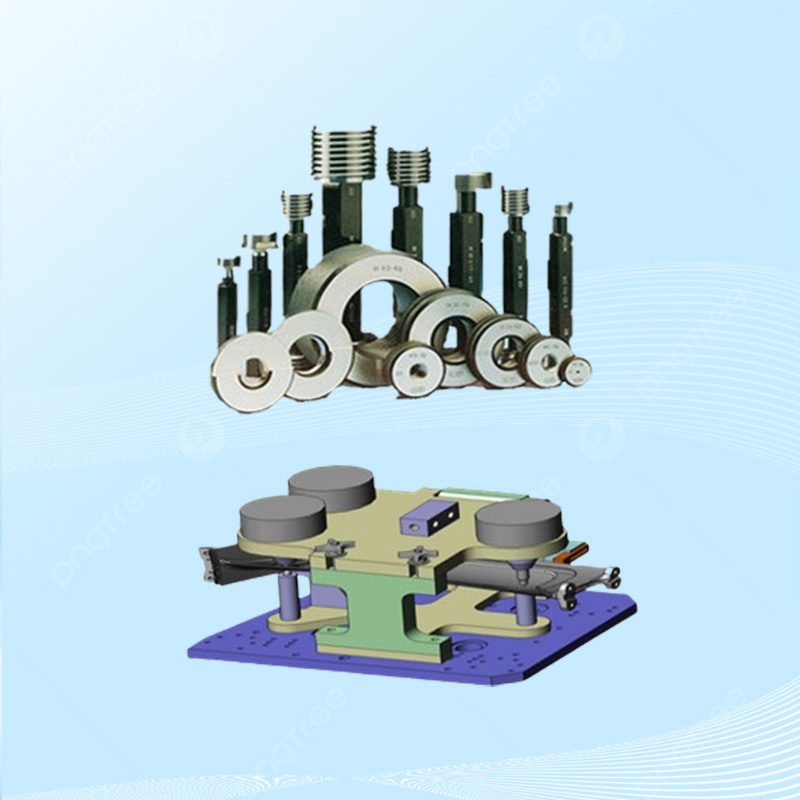
Gauges and fixtures are essential tools in manufacturing and quality control for ensuring that parts and assemblies meet specified dimensions and tolerances. They help maintain consistency, accuracy, and efficiency in production processes. Here's a detailed overview of gauges and fixtures, including their types, uses, and importance:
Gauges
Gauges are measuring instruments used to check the dimensions, shapes, and other physical properties of objects. They are typically used for comparative measurements rather than absolute measurements.
Types of Gauges
- Go/No-Go Gauges:
-
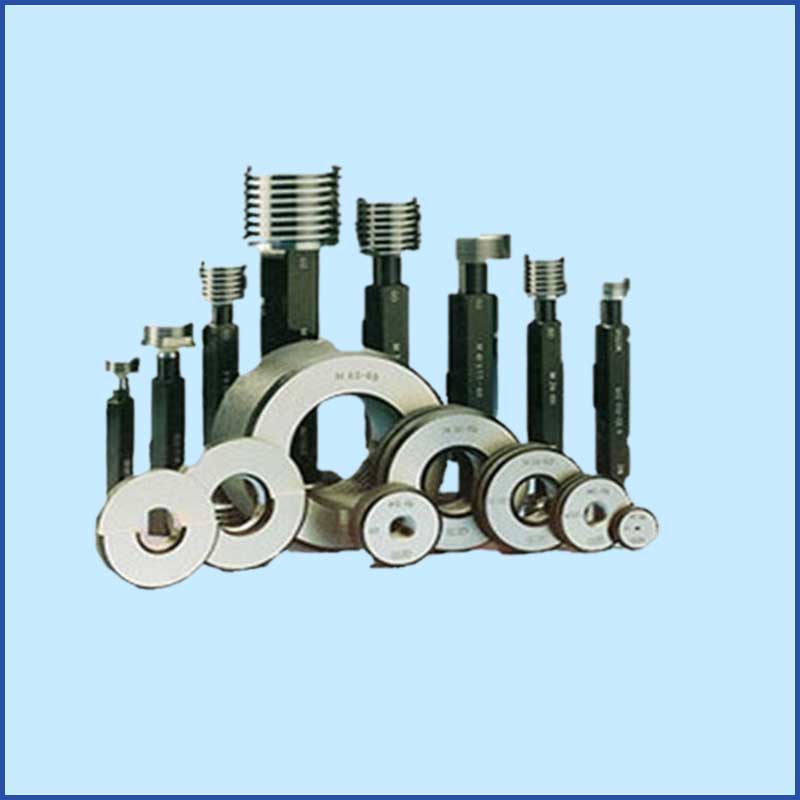
- Plug Gauges: Used to check the diameter of holes. A "Go" gauge should fit into the hole, while a "No-Go" gauge should not.
- Ring Gauges: Used to check the outer diameter of cylindrical parts. Similar to plug gauges but for external dimensions.
- Snap Gauges: Used for quick inspection of external dimensions. They have a "Go" side and a "No-Go" side.
- Thread Gauges:
-
- Thread Plug Gauges: Used to check the internal thread of a part.
- Thread Ring Gauges: Used to check the external thread of a part.
- Thread Pitch Gauges: Measure the pitch or lead of a screw thread.
- Height Gauges:
-
- Measure the height of parts or features from a reference surface. They often include a vernier scale, digital readout, or dial indicator.
- Depth Gauges:
-
- Measure the depth of holes, slots, or recesses. They come in various forms, including micrometer depth gauges and vernier depth gauges.
- Bore Gauges:
-
- Measure the internal diameter of bores. They can be dial bore gauges or digital bore gauges, which provide accurate and repeatable measurements.
- Feeler Gauges:
-
- Consist of thin metal strips of various thicknesses used to measure gap widths or clearances between two parts.
- Radius Gauges:
-
- Used to measure the radius of curves and rounded corners. They come in sets with different radius sizes.
Fixtures
Fixtures are devices used to hold, support, and locate a workpiece during manufacturing or inspection processes. They ensure that parts are consistently positioned and oriented correctly, improving accuracy and repeatability.
Types of Fixtures
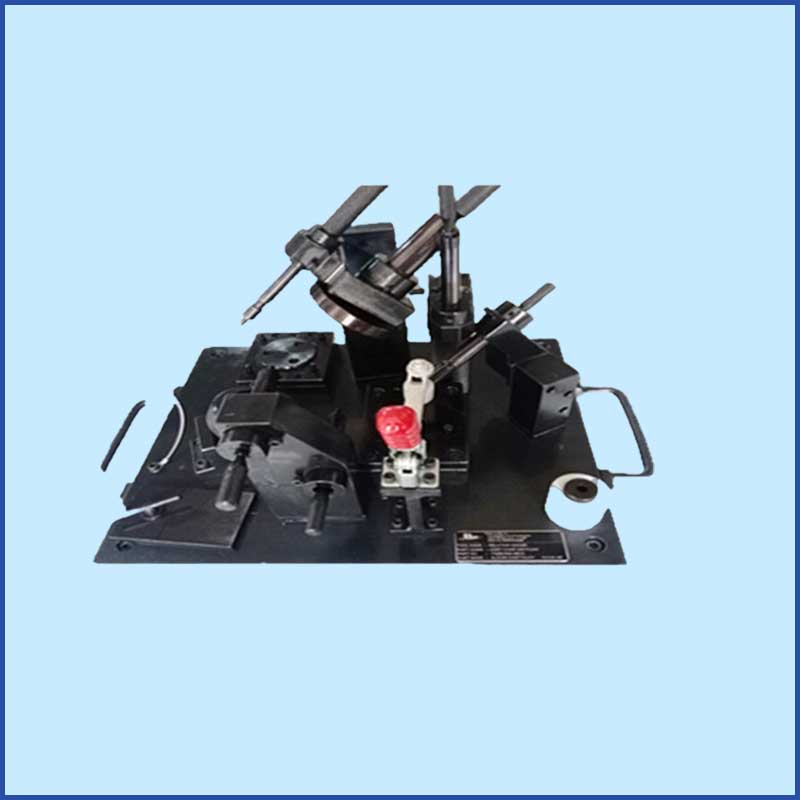
- Inspection Fixtures:
-
- CMM Fixtures: Used to securely hold parts during coordinate measuring machine (CMM) inspection.
- Gauge Fixtures: Custom-made fixtures that hold parts in the correct position for gauging and measurement.
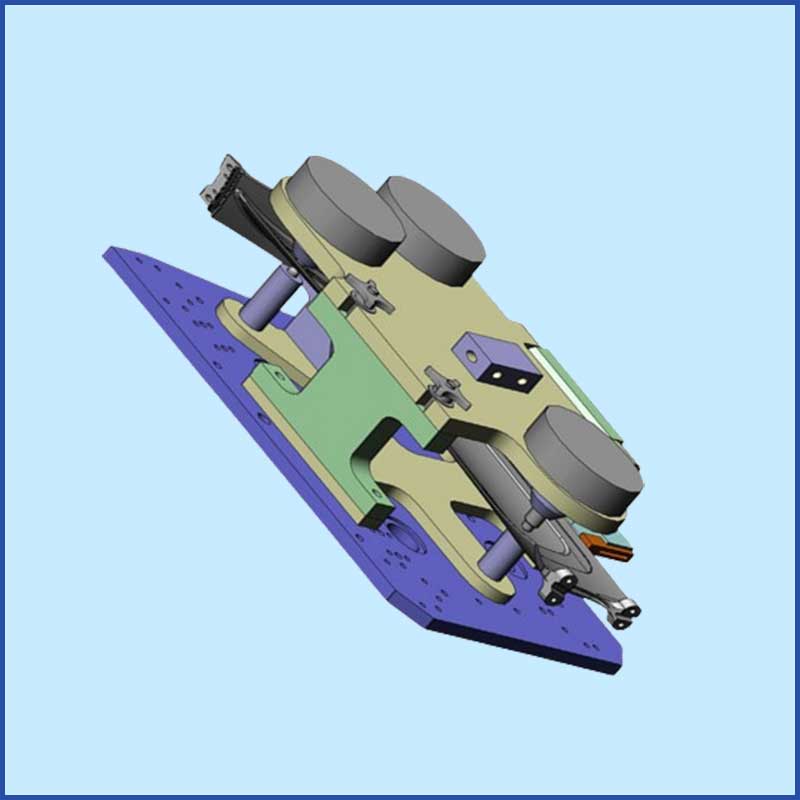
- Machining Fixtures:
-
- Jigs: Guides the tool during machining operations. Common types include drilling jigs and boring jigs.
- Vise Fixtures: Hold workpieces in place during machining. Can be standard vises or custom-made fixtures for specific parts.
- Fixture Plates: Flat plates with a grid of holes or slots used to mount and secure workpieces for various machining operations.
- Assembly Fixtures:
-
- Welding Fixtures: Hold parts in place during welding to ensure correct alignment and positioning.
- Assembly Jigs: Used to position and hold parts during assembly operations, ensuring they fit together correctly.
- Holding Fixtures:
-
- Clamping Fixtures: Use clamps to hold parts securely in place during various operations.
- Magnetic Fixtures: Use magnetic force to hold ferromagnetic workpieces.
Gauges and fixtures are indispensable tools in the manufacturing and quality control industries. They enhance precision, accuracy, and efficiency in production processes, ensuring that parts and assemblies meet the required standards and specifications. By reducing variability, improving consistency, and enabling quick and accurate inspections, gauges and fixtures play a crucial role in maintaining high quality and productivity in manufacturing operations.






